


Of course, the beta of that company not only depends on the activity. In particular, we look for a company that is ‘ purely ‘ engaged in the type project for which we want to estimate the cost of capital. Instead, we can use the equity beta of a publicly traded firm that is engaged in an activity very similar to the project that we are considering.
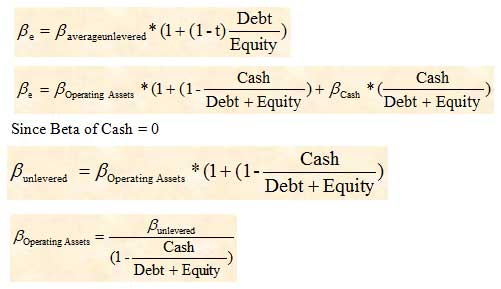
Since specific projects are typically not represented by a publicly traded security, we do not observe the project beta directly. This means that if a project is more risky than average, we should use a higher cost of capital, and vice versa. Why do we use the pure-play method rather than the capital asset pricing model to determine the required rate of return? The reason is that a firm’s average risk is not the same across the different projects that a firm undertakes. At the bottom of the page, we include an Excel spreadsheet example that implements the pure-play method.
Unlevered beta calculator how to#
On this page, we discuss how to apply the pure-play method. In particular, the pure-play method is used to calculate the project beta. The pure-play method is a method used to determine the required rate of return of a project. Present Value of Growth Opportunities (PVGO).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
